Introduction
Airport security has become one of the most critical aspects of modern air travel. As global threats evolve, the need for more advanced and reliable screening systems continues to grow. Central to this effort is the airport security scanner, a technology that has undergone major transformations to enhance both safety and efficiency. This article explores the evolution of airport scanning technology, its current innovations, challenges, and what the future holds for this essential part of air travel security.
A Brief History of Airport Security
The journey of airport security began in the 1970s, a decade marked by rising cases of aircraft hijackings and terrorism. The introduction of metal detectors was a groundbreaking step that allowed security personnel to detect weapons and metallic items on passengers.
However, these early systems had limitations—they could not detect non-metallic threats such as explosives or narcotics.
The tragic events of September 11, 2001, reshaped global airport security. Governments worldwide tightened protocols, leading to the formation of agencies like the Transportation Security Administration (TSA) in the U.S. This new era introduced advanced scanning equipment and comprehensive passenger screening, setting the foundation for today’s technologies.
Major Advancements in Scanning Technology
Modern airport security relies on cutting-edge imaging and detection systems that are far more capable than early detectors.
1. Full-Body Scanners
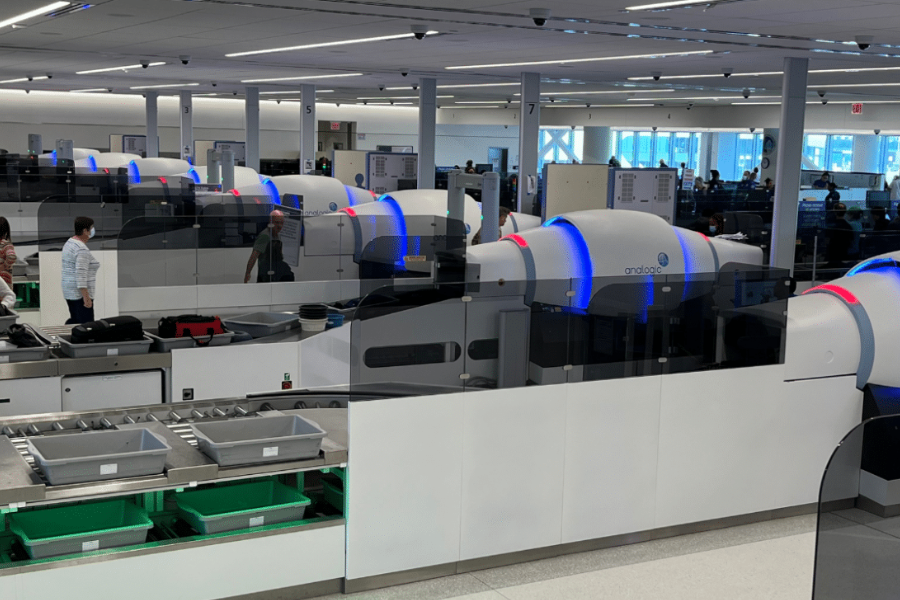
One of the most revolutionary developments is the full-body scanner, which uses millimeter-wave or backscatter radiation to create detailed, real-time images of passengers. These scanners can detect both metallic and non-metallic threats concealed under clothing, making them far more effective in identifying potential dangers.
2. Computed Tomography (CT) Scanners
CT scanners, now widely used for checked baggage screening, generate 3D images that allow for more precise inspections. With this technology, security officers can detect explosives and other prohibited items more accurately, often eliminating the need for manual bag searches—thereby speeding up the screening process.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
AI and machine learning have become integral to airport security. Algorithms can now analyze scanner data in real time, automatically identifying anomalies and reducing false alarms. This improves accuracy, efficiency, and consistency across multiple screening points.
The Role of Biometrics in Airport Security
Biometric technology has transformed the passenger verification process, making travel both safer and smoother.
- Facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and iris recognition are now commonly used to verify passenger identities.
- These systems help automate check-in, boarding, and customs processes, reducing human error and improving overall efficiency.
- Airports like Dubai International and Atlanta Hartsfield-Jackson have successfully integrated biometric gates to shorten wait times and enhance security precision.
As adoption expands, biometric systems are expected to become the global standard for seamless and secure air travel.
Challenges and Ethical Concerns
Despite technological progress, several challenges remain:
1. Privacy Concerns
Full-body scanners and biometric systems have raised privacy and data protection concerns. Critics argue that detailed body scans and facial data could infringe on personal rights. To address this, airports must implement strict data handling protocols and ensure transparency in how passenger data is used, stored, and shared.
2. Training and Human Oversight
Technology alone cannot guarantee security. Security personnel must be properly trained to operate new systems effectively. Without adequate training, even the most advanced equipment may fail to identify threats or be used incorrectly. Continuous skill development is essential to maintain effective airport operations.
The Future of Airport Security Scanning Technology
The future of airport security is focused on speed, accuracy, and passenger convenience.
1. Smart, Predictive Systems
Next-generation scanners will integrate AI with Big Data analytics to predict potential threats before they occur. By analyzing travel history and behavioral patterns, these systems can identify high-risk individuals without intrusive screening.
2. IoT-Enabled Security Networks
The Internet of Things (IoT) will enable interconnected scanners and monitoring devices throughout airports. Real-time data sharing among security checkpoints will improve response times and situational awareness.
3. Non-Invasive Scanning
Future research is exploring non-intrusive scanners capable of detecting weapons or explosives without requiring passengers to remove shoes, belts, or jackets. This innovation would greatly improve the travel experience while maintaining high safety standards.
Collaborative Efforts for Safer Skies
The continuous improvement of airport security depends on collaboration between governments, security agencies, and technology companies. By sharing research, intelligence, and innovations, stakeholders can stay ahead of evolving threats. International cooperation will also help standardize best practices and ensure consistent security measures across airports worldwide.
Conclusion
The evolution of airport security scanning technology has redefined how the world safeguards air travel. From early metal detectors to AI-powered, biometric-driven systems, every advancement has aimed to make flying safer and more efficient.
As we move forward, airports must balance security, privacy, and convenience. The integration of smart technologies promises a future where air travel is both highly secure and seamlessly connected—offering passengers peace of mind and a smoother journey from check-in to take-off.